Jupiter's north pole seen by Juno spacecraft
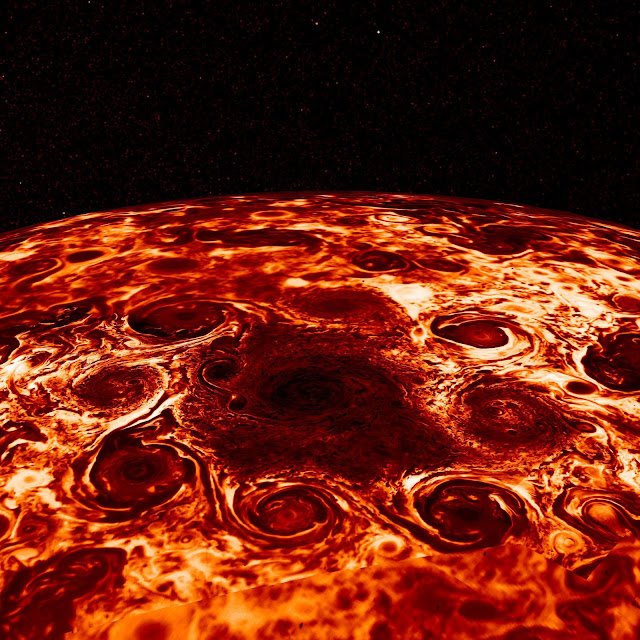
In this composite image, derived from data collected by the Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument aboard NASA's Juno mission to Jupiter, shows the central cyclone at the planet's north pole and the eight cyclones that encircle it. JIRAM collects data in infrared, and the colors in this composite represent radiant heat: the yellow (thinner) clouds are about 9 degrees Fahrenheit (-13° Celsius) in brightness temperature and the dark red (thickest) are around -181 degrees Fahrenheit (-118.33° Celsius). Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/ASI/INAF/JIRAM Explanation from: https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22335